Yes, notes receivable are typically classified as current assets if they are expected to be collected within one year. This is because current assets are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within a relatively short period, usually within 12 months. Some companies will issue zero-interest-bearing notes as a sales incentive. Even though the interest rate is not stated, the implied interest rate can normal balance be derived because the cash values lent and received are both known. In most cases, the transaction between the issuer and acquirer of the note is at arm’s length, so the implicit interest rate would be a reasonable estimate of the market rate.
Understanding and Managing Notes Receivable in Financial Reporting

The carrying amount of the note may be adjusted for amortization of discounts or premiums, and for any allowance for credit losses. The allowance reflects management’s estimate of the likelihood that some receivables will not be collected and is based on historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts. Notes receivables are written promissory notes which give the holder or bearer the right to receive the amount mentioned in the agreement.
Journal Entry at month end February
For scenario 2, the principal is being reduced on an annual basis, but the payment is not made until the end of each year. For scenario 3, there is an immediate reduction of principal due to the first payment of $1,000 upon issuance of the note. The remaining four payments are made at the beginning instead of at the end of each year.
Journal Entries for Notes Receivable
- Now let’s look at what happens when the customer in Situation 2a above finally pays the company back after the period.
- Notes receivable come in the form of a written document that borrowers pay to their lenders.
- A note receivable is an unconditional written promise to pay a specific sum of money on demand or on a defined future date and is supported by a formal written promissory note.
- From the side of the maker of the notes, it is known as the notes payable as he must pay the specific sum of money at a specified future date to the holder of the notes receivable.
For Notes due in less than one year, Notes Receivable accounts are listed in the Current Asset section of the Balance Sheet. Notes Receivable due in more than one year are listed in the Long-term Asset section of the Balance Sheet. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written Bookstime for most major financial media publications.

Are the Accounts Receivable Current or Non-assets?
- Determining present values requires an analysis of cash flows using interest rates and time lines, as illustrated next.
- These solutions enable businesses to automate their entire account receivable process, accelerating cash flow, improving efficiency, and reducing operational costs.
- The maker is another business or debtor who signs a legal agreement to repay the debt, including interest charges.
- For the purposes of accounting class, we will focus on Accounts Receivable transactions where an Accounts Receivable is turned into a Note Receivable.
- For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing.
It is important to note that this accrued interest is recognized as a separate line item from the principal amount of the notes receivable, ensuring clarity in the financial statements. X ltd. sold machinery to Y Ltd for $ 500,000 with the terms that payment against purchase will be made within 35 days from the date of sale. However, even after 35 days, Y ltd could not make the payment of the specified amount to the X ltd. Hence, with the consent of both of the parties, it was decided that X ltd will receive the notes receivable with a principal amount of $ 500,000 and a 10% interest rate to be issued by Y Ltd.
Notes Receivables – Definition, Importance, Example, and Classification
- In the following example, a company received a 60-day, 12% note for $1,000 from a customer on account on January 1.
- Note receivable is the better option because there is a very high chance of getting payment on time with the note receivable as compared to the simple credit transaction.
- Notes can be converted to cash by discounting them to the financial institutions.
- Notice that the sign for the $7,835 PV is preceded by the +/- symbol, meaning that the PV amount is to have the opposite symbol to the $10,000 FV amount, shown as a positive value.
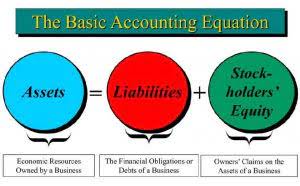
- The higher the proportion of current assets in relation to total liabilities, the greater the company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations.
- A deferred tax is reversed when the expense is deducted for tax purposes or when revenue or gain is recognised in the income statement.
- Cash is the most liquid asset of an entity and is therefore important for the short-term solvency of a company.
Note receivable can be used as evidence in legal proceedings and includes some interest rate that works as an investment. Notes receivable can be treated as either is note receivable a current asset current assets or non-current assets depending on the timelines and intention of the company. Proper classification of notes receivable is vital for budgeting, forecasting, and decision-making purposes. It also ensures that you have an accurate representation of your company’s liquidity position.
